Overview of the Bank of Canada's Role in the Economy
Understanding the Bank of Canada's Monetary Policy
The Bank of Canada is the nation's central bank. Its main role is to promote the economic and financial well-being of Canada.
One of its key responsibilities is to conduct monetary policy. This involves managing the supply of money and credit in the economy to keep inflation low and stable.
How Interest Rates Influence Economic Activity
Interest rates are a powerful tool in the Bank of Canada's monetary policy toolkit. By adjusting the target for the overnight rate, the Bank influences other interest rates in the economy.
These changes affect borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, impacting spending, investment, and overall economic activity. For instance, lowering interest rates makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging spending and investment. This can stimulate economic growth.

Impact of Interest Rate Decisions on Personal Finances
Effects on Mortgage Rates and Housing Market
Interest rate decisions have a direct impact on mortgage rates. When the Bank of Canada cuts interest rates, it becomes cheaper to borrow money. This often leads to lower mortgage rates.
Lower mortgage rates can make homeownership more affordable. The housing market tends to become more active.
Variable vs. Fixed Mortgage Rates
Variable mortgage rates are directly tied to the Bank of Canada's overnight rate. They fluctuate as the central bank adjusts its policy rate.
Fixed mortgage rates, on the other hand, are influenced by bond yields. They tend to be less responsive to short-term changes in the Bank of Canada's rate.
Predictions for Mortgage Costs in 2025
Many economists predict that the Bank of Canada will continue to cut rates in 2025. This is according to the article, "2025 mortgage predictions - and some wishful thinking."
This could lead to lower mortgage rates, potentially making it a good time for homebuyers. However, fixed rates might remain relatively stable due to high bond yields.
Implications for Consumer Debt and Spending
Interest rate changes also affect consumer debt and spending. Lower rates can make it cheaper to carry debt, such as credit card balances or lines of credit.
This can free up disposable income for consumers. It might lead to increased spending. Conversely, higher rates can increase the cost of debt, potentially dampening consumer spending.
Interest Rates and Economic Growth
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Inflation
The Bank of Canada uses interest rates as a primary tool to control inflation. When inflation is high, the Bank may raise rates to cool down the economy and bring inflation back to its target.
Conversely, when inflation is low, the Bank may lower rates to stimulate economic activity. This helps prevent deflation.
How Rate Changes Control Inflation
Higher interest rates reduce borrowing and spending, which can help to slow down price increases. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, potentially boosting inflation.
The Bank of Canada aims to keep inflation at 2 per cent. This is the midpoint of a 1-to-3 per cent target range.
Historical Context of Inflation Targeting in Canada
Canada was one of the first countries to adopt inflation targeting in the early 1990s. This approach has been largely successful in keeping inflation low and stable.
"Evaluating our approach to monetary policy" highlights the success of inflation targeting. It emphasizes its role in maintaining price stability and fostering economic growth.
Predictions for Economic Growth in 2025
Economic growth in 2025 is expected to be influenced by the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions. With anticipated rate cuts, economic growth could be supported.
The article "Year ahead in Canada: Return to growth as rate cuts take hold" suggests that growth could reach around 2 per cent in 2025. This is due to accommodative monetary policy.
Expected Outcomes from Recent Rate Cuts
Recent rate cuts are expected to stimulate investment and consumer spending. Lower financing costs can encourage businesses to expand and invest in new projects.
For consumers, lower mortgage rates and reduced debt servicing costs can boost disposable income. This could lead to higher consumer spending.
Future Outlook: What to Expect from the Bank of Canada
Predictions for Interest Rates in 2025
Many analysts predict that the Bank of Canada will continue to cut interest rates in 2025. The goal is to support economic growth and keep inflation close to the 2 per cent target.
The "Year ahead in Canada" article forecasts that the policy rate could fall to 2.75 per cent. This would be within the first half of the year.
Factors Influencing Future Rate Decisions
Several factors will influence the Bank of Canada's future rate decisions. These include inflation trends, economic growth, the labour market, and global economic conditions.
The Bank also considers factors such as household debt levels and the housing market. They monitor the impact of previous rate changes on the economy.
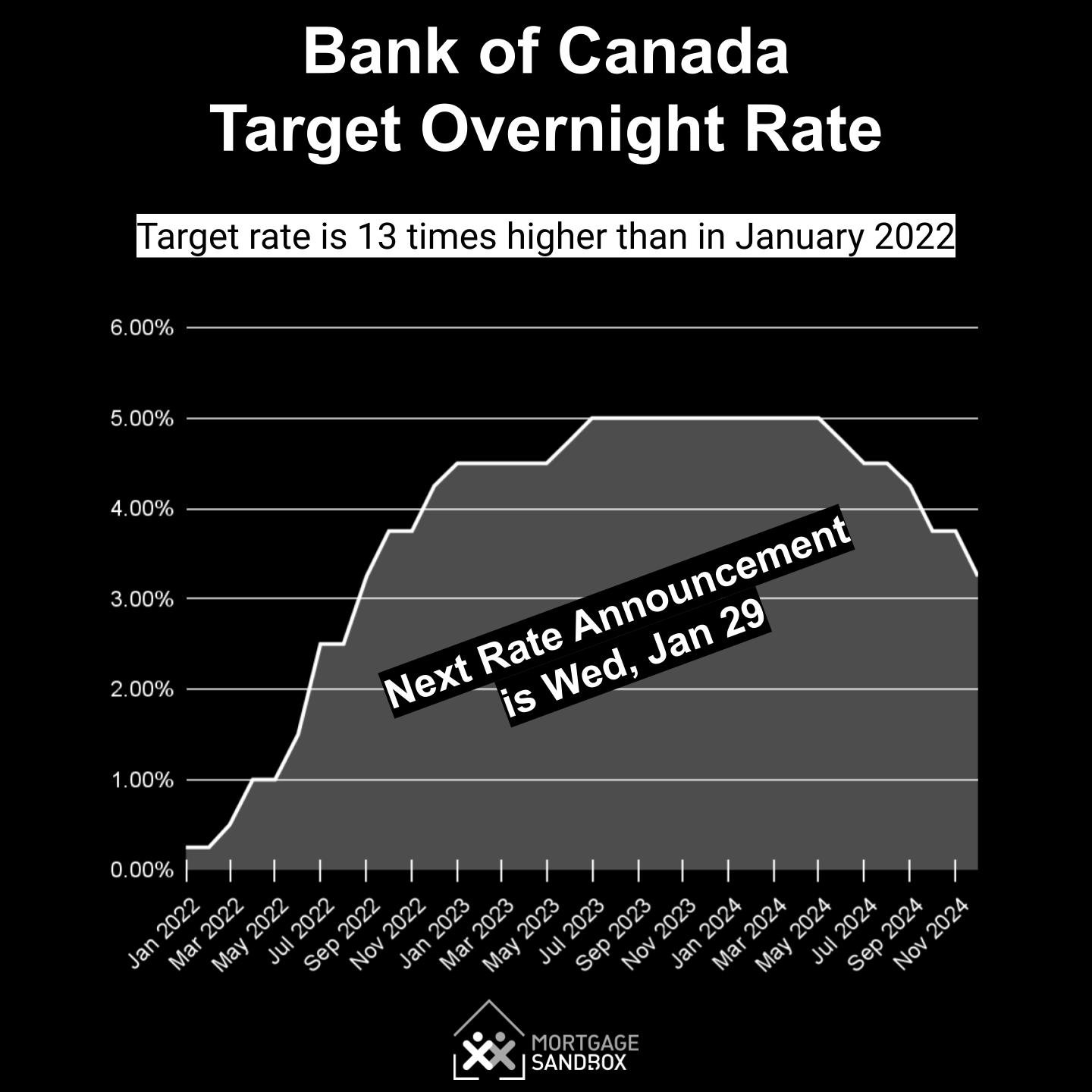
Potential Economic Scenarios Based on Rate Changes
If the Bank of Canada continues to cut rates, it could lead to a more robust economic expansion. Lower rates could stimulate business investment and consumer spending, driving growth.
However, there are risks to consider. If rates are cut too aggressively, it could lead to higher inflation. The Bank must carefully balance the need to support growth with the need to maintain price stability.
How Canadians Can Prepare for Rate Changes
Financial Strategies for Homeowners
Homeowners can prepare for potential rate changes by considering their mortgage options. Those with variable-rate mortgages may benefit from further rate cuts.
Homeowners with fixed-rate mortgages might consider refinancing if rates fall significantly. It's important to assess individual financial situations and consult with a financial advisor.
Managing Personal Finances in a Changing Economy
In a changing economic environment, it's crucial to manage personal finances wisely. This includes budgeting, saving, and managing debt effectively.
Consumers should be mindful of their spending and borrowing. Diversifying investments can also help mitigate risks associated with interest rate changes.
Conclusion: The Long-Term Effects of Interest Rate Policies
Summary of Key Points
The Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions have far-reaching effects on the economy and personal finances. Rate changes influence mortgage rates, consumer debt, inflation, and economic growth.
In 2025, further rate cuts are expected, which could support economic expansion. Canadians should stay informed and adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
Final Thoughts on Financial Planning in Response to Rate Changes
As the economy evolves, proactive financial planning is essential. Understanding the potential impacts of interest rate changes can help individuals make informed decisions.
Staying informed about economic trends and seeking professional advice when needed can contribute to long-term financial well-being. Fintech innovations are also shaping the banking sector. You can learn more about this in our post, "10 Game-Changing Fintech Innovations Shaping Banking in 2025."
Key Takeaways:
- The Bank of Canada uses interest rates to manage inflation and stimulate economic growth.
- Rate cuts in 2025 could lead to lower mortgage rates and increased consumer spending.
- Economic growth in 2025 is projected to be around 2%, driven by accommodative monetary policy.
- Canadians should adapt their financial strategies to navigate the changing economic landscape.
- Inflation targeting has been successful in maintaining price stability in Canada since the early 1990s.
