How Blockchain Integration is Transforming Financial Systems for the Future
Understanding Blockchain Technology in Finance
Definition of Blockchain and Its Core Principles
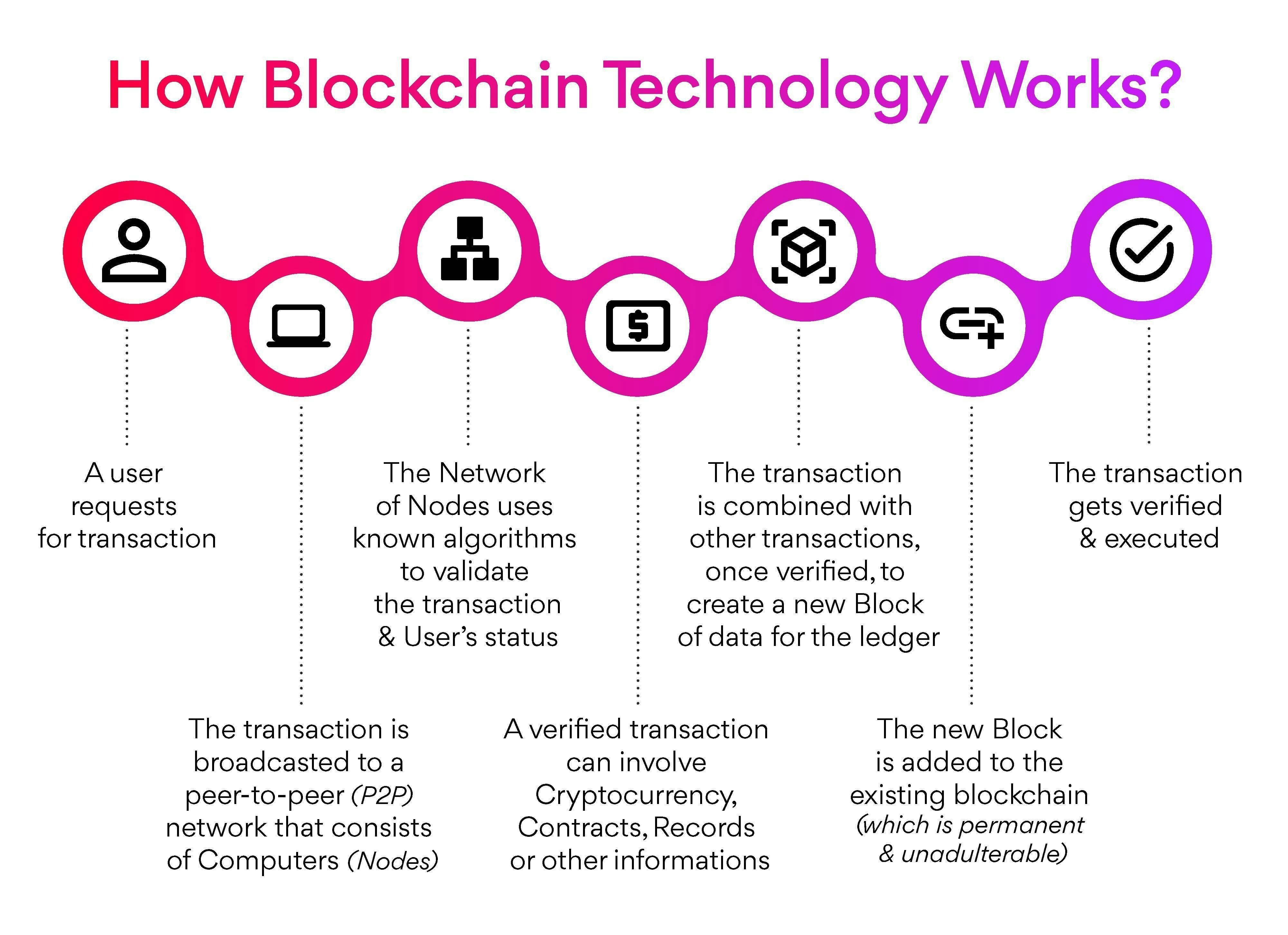
Blockchain is a decentralized, secure digital ledger. It records transactions across a network of computers.
Each transaction is recorded in a chronological chain of blocks. These blocks are linked together and secured through cryptography.
How Blockchain Differs from Traditional Financial Systems
Traditional financial systems rely on centralized authorities. Blockchain eliminates this need.
It offers a peer-to-peer network. This enhances transparency and reduces the risk of fraud.
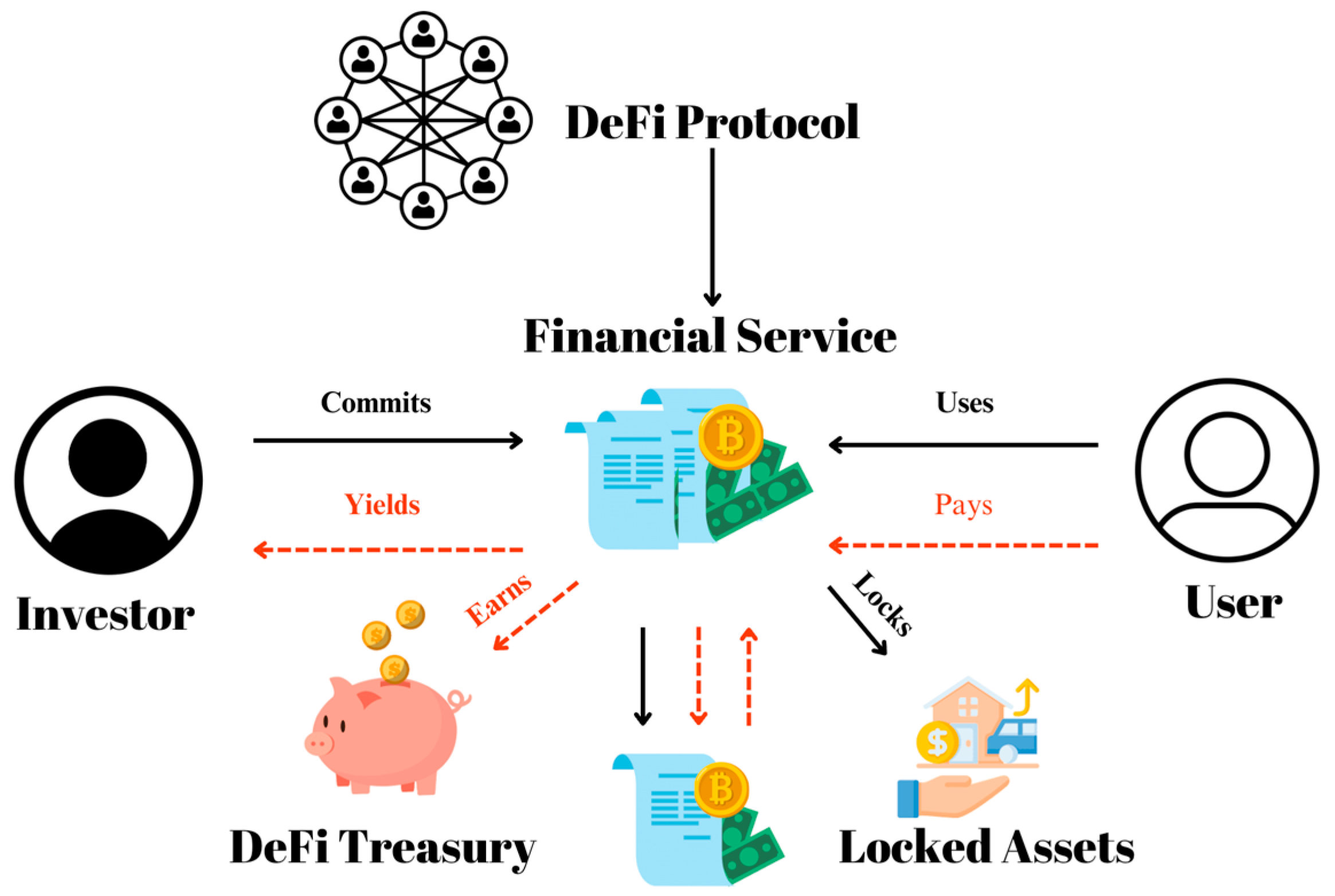
Impact of Blockchain on Financial Services
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Blockchain's decentralized nature ensures higher security. It reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
Transactions are encrypted. They are linked to previous transactions, making it difficult to alter data.
Increased Efficiency in Transactions and Processes
Blockchain facilitates real-time transactions. It improves cash flow and reduces delays.
Banks can bypass intermediaries. This allows customers to complete transactions more quickly.
Transformation of Asset Management and Ownership
Blockchain enables the tokenization of assets. Examples include real estate and stocks.
These tokens can be traded on blockchain platforms. It enables fractional ownership and increases liquidity.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Banking
Cost Reduction and Streamlined Operations
Blockchain can reduce infrastructure costs. Juniper Research reports potential savings of over $27 billion by 2030 in cross-border settlement transactions.
Smart contracts automate processes. This minimizes manual intervention and cuts costs.
Improved Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain provides an immutable record of all transactions. It enhances transparency.
This traceability is crucial for businesses. It ensures compliance with legal and regulatory standards.
Innovations in Customer Experience and Service Delivery
Blockchain simplifies loan approvals. It provides transparent records of creditworthiness.
Identity verification becomes more efficient. Payment processes are accelerated, reducing transaction times.
.jpg)
Future Trends in Blockchain for Finance
Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is a rapidly growing sector. It allows users to access financial services without relying on traditional institutions.
DeFi platforms are built on decentralized networks. They provide greater control over assets.
Growth of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central banks are exploring digital currencies. The Swedish Central Bank is experimenting with the e-krona.
These initiatives aim to explore the implications of introducing a CBDC. They offer faster transactions and support financial inclusion.
Advancements in Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts automate contract terms. They reduce the need for third-party enforcement.
This automation can significantly reduce costs. It also reduces human error in financial transactions.
Challenges of Integrating Blockchain in Financial Systems
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Issues
The regulatory landscape for blockchain is complex. Different countries have varying legal frameworks.
Banks must navigate these complexities. They must establish clear guidelines for blockchain adoption.
Interoperability with Existing Systems
The banking industry relies on a complex network of systems. Many are not compatible with blockchain.
Adopting standardized protocols can facilitate interoperability. Banks can also participate in industry consortia.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Blockchain's transparency can be a drawback. Data privacy is paramount in banking.
Banks can implement permissioned networks. They can use cryptographic techniques to protect sensitive data.
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain in Banking
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
Blockchain enables faster and cheaper cross-border transactions. It eliminates intermediaries and reduces settlement times.
Ripple offers a blockchain-based solution. This allows banks to bypass the traditional SWIFT network.
Trade Finance and Supply Chain Management
Blockchain simplifies trade finance. It digitizes the entire process, from issuing letters of credit to verifying documents.
HSBC implemented a blockchain-based platform. It enables secure sharing of trade documents.
Tokenization of Assets and Digital Securities
Blockchain allows for the tokenization of real-world assets. Banks can issue tokenized assets on blockchain platforms.
This facilitates faster settlement. It enhances liquidity in financial markets.
Conclusion
The Future Landscape of Financial Systems with Blockchain Integration
Blockchain technology is set to transform financial systems. Its decentralized nature offers enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency.
As the technology matures, it will redefine processes. It will create new paradigms where value is brought at every touch point.
Call for Continuous Innovation and Adaptation in Financial Institutions
Financial institutions must embrace blockchain. They must adapt to stay competitive.
Continuous innovation is essential. The future of finance with blockchain integration is promising. You can read more about this topic in this article on "Exploring the Latest Trends in Blockchain Integration for Financial Systems".
Key Takeaways:
- Blockchain offers enhanced security through its decentralized and immutable ledger.
- Transactions are faster and more efficient with blockchain, reducing costs and delays.
- Tokenization of assets increases liquidity and creates new investment opportunities.
- DeFi and CBDCs are emerging trends that will shape the future of finance.
- Regulatory and interoperability challenges need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
