Exploring The Latest Trends In India's Economic Growth And Rural Consumer Spending
Economics professor providing insights into fiscal policies and market behavior.

Economics professor providing insights into fiscal policies and market behavior.

— in Sustainability
— in Economics
— in Personal Finance
— in Tech Industry Insights
— in Entrepreneurship
India's economy has shown remarkable resilience and growth in 2024. Real GDP growth climbed to 8.4% year-over-year in the third quarter of the fiscal year. This is a testament to the country's robust domestic demand.
Private investment spending grew by 10.6% year-over-year. This indicates a strong boost to the private capital expenditure cycle.
A key indicator of India's economic health is the growth in private investment. Investment growth remained above 8% year-over-year in the last four quarters. High capital expenditure by the government is expected to crowd in private investments.
Another indicator is private consumption, which improved to 3.5% year-over-year. The index of industrial production of consumer durables indicated a revival in private consumption.
Manufacturing and construction activities have been strong contributors to India's GDP. Manufacturing grew by 11.6% year-over-year, and construction by 9.5% year-over-year. Services also performed steadily, growing at 7% year-over-year.
However, agriculture contracted by 0.8% year-over-year, weighing on the economy. This was partly due to temporal rains impacting kharif crop production.
Rural India has emerged as a significant driver of consumer demand. In the July-September quarter, rural demand grew twice as fast as urban demand. Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) growth in rural India has outpaced urban growth for several quarters.
Companies are expanding their reach to India's hinterland. Rural India's growing consumption is boosting the demand for FMCG products.
Urban demand has been a mixed bag, with mass-market segments showing signs of strain. High food inflation is eating into household budgets in urban areas. The urban-rural monthly per capita consumer spending gap narrowed to 70% in 2023/24 from 84% in 2011/12.
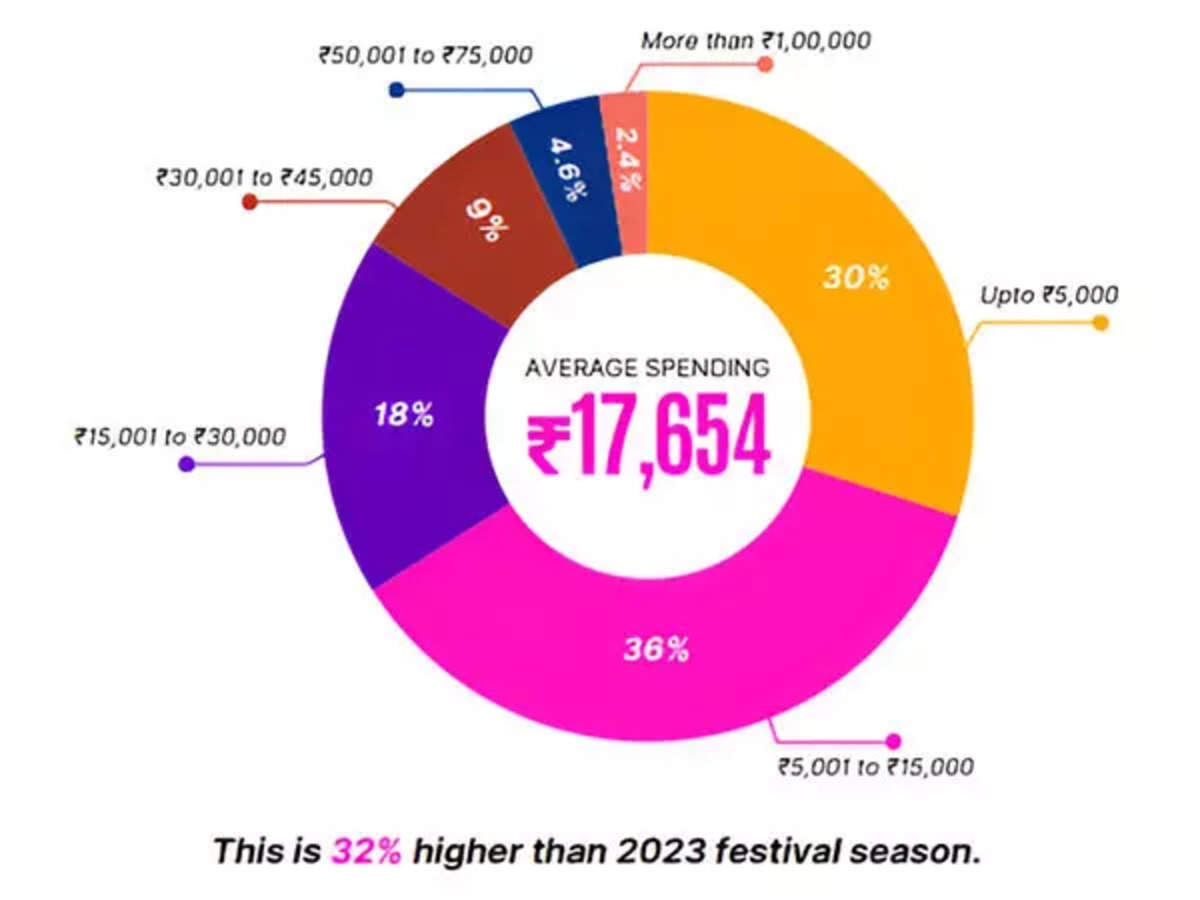
In nominal terms, rural consumer spending climbed 9.55% year on year. Urban spending rose 8.31%, according to a government report.
Improved weather conditions and diversified income sources have contributed to rural growth. Government initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) have also played a role. This program facilitated employment for 11.37 crore households.
The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme provides financial assistance to farmers. These initiatives have helped improve the financial stability of rural households.
India's IT sector continues to be a major growth driver. Companies are accelerating their digital transformation, adopting cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity solutions. The Indian government's push for a Digital India is fostering innovation.
Increased global demand for digital services has led to higher outsourcing of IT services to India. This sector is expected to contribute significantly to employment and foreign exchange earnings.
India has made substantial investments in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Government support through initiatives like the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) is promoting growth. Technological advancements are making renewable energy more cost-competitive.
India is poised to become a global leader in clean energy. The renewable energy sector is expected to continue its rapid growth.
E-commerce in India is expanding rapidly, fueled by increasing internet penetration. Changing consumer behavior and the growth of digital payment infrastructure are also driving this trend. The rise of online shopping platforms has transformed the retail landscape.
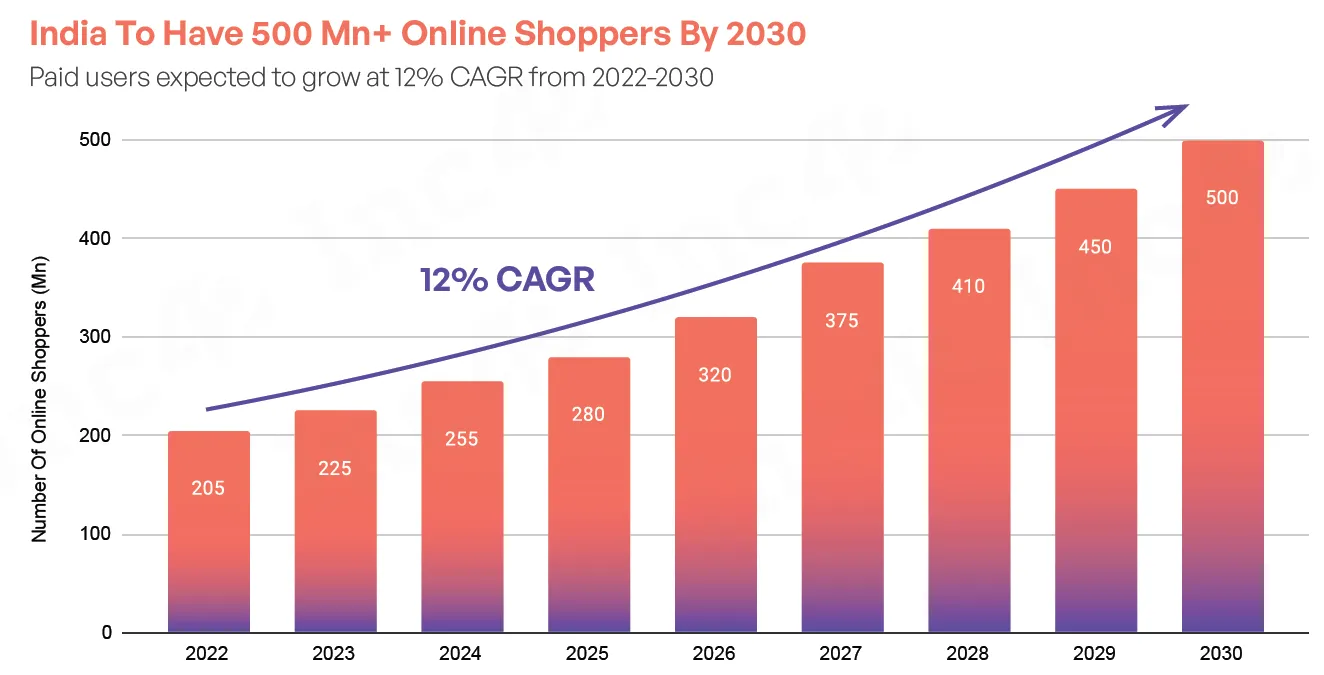
As internet access becomes more widespread, both urban and rural consumers are shifting to online shopping. The rapid adoption of digital payment systems like UPI has facilitated online transactions.
India's healthcare and biotechnology sector is one of the fastest-growing. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of robust healthcare systems. India is witnessing rapid advancements in healthcare delivery and biotechnology.
The government's Ayushman Bharat scheme aims to provide health coverage to millions. Biotechnology research and development are seeing rapid growth in areas like genomics and vaccine development.
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to boost rural economic development. The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) guarantees at least 100 days of wage employment in a financial year. The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) provides direct financial assistance to farmers.
The Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) aims to enhance rural connectivity. These initiatives aim to improve livelihoods and infrastructure in rural areas.
Despite these efforts, challenges persist in policy implementation. Programs are often implemented by various departments with insufficient coordination. Fund leakage due to corruption and mismanagement is a significant issue.
Beneficiary identification and selection criteria are often flawed. Rural workers often experience delayed payments, which harms the long-term efficacy of projects.
Hiware Bazar in Maharashtra is a notable success story. Through community-driven efforts, the village implemented water conservation techniques. This boosted agricultural productivity and enhanced the overall quality of life.
Similar success stories can be found in Kawadgaon village in Maharashtra and Thiruvankulam in Kerala. These examples highlight the importance of community involvement in rural development.
India is expected to grow between 7.6% and 7.8% in fiscal 2024. Private investments will likely gain momentum later this year. A synchronous global recovery next year will likely help improve exports.
Inflation concerns are likely to persist in the short term. However, as private investment kicks in, the supply side will improve, and prices are expected to come down.
Rural markets are playing an increasingly important role in shaping economic policies. The growth in rural consumer demand is influencing companies to expand their reach to rural areas. The government is also focusing on policies that support rural development.
Initiatives like MGNREGA and PM-KISAN are aimed at improving rural livelihoods. These policies are crucial for achieving balanced economic growth.
Prudent consumer spending is essential for sustainable growth. More employment opportunities in rural areas can help increase savings. The movement of disguised employment away from agriculture to manufacturing will likely improve income prospects.
Government spending on infrastructure projects is expected to create jobs. The government's emphasis on upskilling and reskilling in emerging technologies will also contribute to better employability.
Key Takeaways: