How Is Bitcoin Actually Mined? A Simple Explanation
Financial writer covering the latest trends in global economics and cryptocurrency.
Financial writer covering the latest trends in global economics and cryptocurrency.

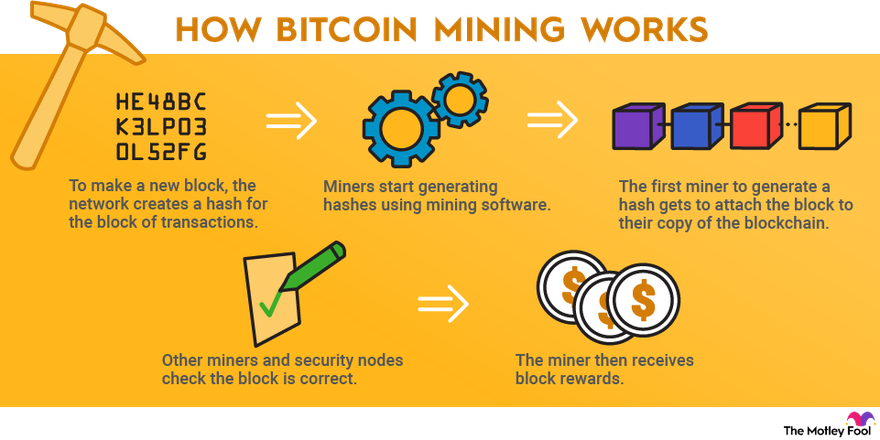
Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions on the Bitcoin network and adding them to the blockchain. It involves complex mathematical calculations that require substantial computational power. By solving these puzzles, miners help maintain the integrity of the network while earning new bitcoins as a reward.
The primary purpose of Bitcoin mining is twofold: it secures the network and introduces new bitcoins into circulation. Each time a miner successfully adds a new block to the blockchain, they validate all transactions within that block, ensuring that the same bitcoin isn’t spent twice. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for a central authority, making Bitcoin a robust and secure currency.
Miners act as auditors for the Bitcoin network. They compete to solve cryptographic puzzles, and the first to solve one gets to add the block and receive the associated rewards. This competition not only secures the network but also incentivizes miners to invest in powerful hardware and energy resources.
When a transaction occurs, it is grouped with other transactions into a block. Miners then verify these transactions by checking their validity against the blockchain. Only transactions that meet the network’s criteria are included in the block.
Hashing is a crucial part of the mining process. Each block contains a unique hash, generated from the transaction data, the previous block’s hash, and a nonce (a random number used once). Miners continuously adjust the nonce to find a hash that meets the network's difficulty target.
Bitcoin employs a proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism to ensure that mining requires significant computational effort. This method deters spam and malicious attacks by making it costly to generate new blocks. The first miner to solve the PoW puzzle gets to add the block to the blockchain and receive the reward.
Currently, miners receive a reward of 3.125 bitcoins for each block mined, a figure that halves approximately every four years in an event known as "halving." This mechanism regulates the supply of Bitcoin, ensuring that the total number of bitcoins never exceeds 21 million.
To begin mining, you need powerful hardware. The two main types are ASIC miners and GPUs.
As of 2024, the Bitmain Antminer S21 Hyd is considered the most profitable mining machine, boasting a hash rate of 335 TH/s. Other notable models include the Canaan Avalon A1266 and MicroBT Whatsminer M50S.
| Mining Hardware | Hashrate | Power Consumption (Watts) | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitmain Antminer S21 Hyd | 335 TH/s | 5360 | $4,200 |
| Canaan Avalon A1266 | 130 TH/s | 3250 | $5,499 |
| MicroBT Whatsminer M50S | 126 TH/s | 3276 | $2,999 |
Mining requires specific software to connect your hardware to the Bitcoin network. Popular options include CGMiner, BFGMiner, and EasyMiner.
Joining a mining pool allows miners to combine their computational power, increasing the chances of earning rewards. However, the earnings are shared among all pool members, which can reduce individual profits.
To mine Bitcoin at home, you’ll need to set up a mining rig. This involves assembling the necessary hardware and installing the mining software.
Selecting the right hardware is crucial. High-performing ASIC miners are recommended for better efficiency and profitability.
The cost of setting up a mining operation can be substantial, often exceeding $10,000 for a competitive rig. Additionally, electricity costs can significantly impact profitability.
Once you have your hardware, you need to configure your mining software to connect to your chosen mining pool and set up your wallet for receiving rewards.
Joining a mining pool, such as Slush Pool or Antpool, can enhance your chances of earning rewards. Pools share the workload, making it easier to find blocks.
Bitcoin mining is energy-intensive, consuming around 176 terawatt-hours annually, comparable to the energy consumption of entire countries. The reliance on fossil fuels contributes to a significant carbon footprint.
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining has sparked debates about sustainability. Critics point out the high energy consumption and resulting emissions, while proponents argue that mining can promote renewable energy use.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental effects of Bitcoin mining include using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, and adopting more energy-efficient mining technologies.
The future of Bitcoin mining will likely be shaped by technological advancements and regulatory developments. As mining difficulty increases, miners must adapt to remain profitable.
Cryptocurrency mining continues to evolve, with new hardware and software constantly emerging. Staying informed about industry trends and environmental considerations will be crucial for future miners.
Key Takeaways:
— in Cryptocurrency
— in Cryptocurrency
— in Cryptocurrency
— in Cryptocurrency
— in Cryptocurrency